Lunar tides are one of the most captivating natural phenomena that have fascinated scientists, sailors, and everyday observers for centuries. These tides, primarily driven by the gravitational pull of the Moon, play a crucial role in shaping the Earth's natural environment, influencing everything from oceanic currents to coastal ecosystems. Despite their everyday occurrence, lunar tides remain a profound example of the delicate balance that governs our planet's interconnected systems.
The intricate dance between the Earth, Moon, and Sun gives rise to these rhythmic movements of water, creating high and low tides across the globe. But lunar tides are more than just rising and falling water levels—they are a testament to the celestial mechanics that govern our universe. Their impact extends far beyond coastal waters, affecting marine life, human activities, and even the Earth's rotation over geological time scales.
In this article, we’ll delve into the mechanics behind lunar tides, their historical significance, and their role in shaping our planet. Whether you’re a student, a curious learner, or an enthusiast of natural wonders, this in-depth guide will help you understand the science, impact, and future implications of lunar tides in our ever-changing world.
Table of Contents
- What Are Lunar Tides?
- How Do Lunar Tides Work?
- What Causes High and Low Tides?
- The Role of the Moon in Lunar Tides
- How Solar Tides Interact with Lunar Tides?
- Spring and Neap Tides Explained
- Lunar Tides and the Earth's Rotation
- How Do Lunar Tides Affect Marine Life?
- Historical and Cultural Significance of Lunar Tides
- Lunar Tides and Human Activities
- Lunar Tides and Coastal Ecosystems
- Technological Advancements in Tide Prediction
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Are Lunar Tides?
Lunar tides refer to the periodic rise and fall of sea levels caused primarily by the Moon's gravitational pull on Earth. These tides are a direct result of the gravitational interaction between the Earth and its celestial companion, the Moon. While the Sun also contributes to tidal forces, the Moon's proximity to Earth makes it the dominant force behind this phenomenon.
The movement of water during lunar tides occurs in predictable patterns, which have been studied and documented for centuries. These patterns are influenced by the relative positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun, as well as the Earth's rotation. Lunar tides are a key component of the Earth's hydrological system, affecting not just oceans but also lakes, rivers, and even underground water reservoirs.
Defining Tides in Simple Terms
In simple terms, tides are the periodic rising and falling of water levels in oceans and other large water bodies. Lunar tides, in particular, are those caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon. The term "lunar tides" is used to distinguish these from solar tides, which are caused by the Sun's gravitational influence.
Interestingly, lunar tides occur in a cyclical pattern roughly every 24 hours and 50 minutes. This period is slightly longer than a standard day because it accounts for the Moon's orbit around the Earth. This cycle gives rise to two high tides and two low tides in most coastal areas within a single day.
How Do Lunar Tides Work?
The mechanics of lunar tides are rooted in the laws of physics, particularly the principles of gravitational attraction and centrifugal force. To understand how lunar tides work, it's essential to consider the interplay between these two forces.
The Gravitational Pull of the Moon
The Moon exerts a gravitational force on the Earth, which is strongest on the side of the Earth closest to the Moon. This gravitational pull causes the water on this side to bulge outward, creating what is known as a high tide. Meanwhile, on the opposite side of the Earth, a secondary high tide occurs due to the centrifugal force generated by the Earth-Moon system's rotation.
The Role of Centrifugal Force
While gravity pulls water toward the Moon, the Earth's rotation creates a centrifugal force that pushes water outward on the side opposite the Moon. This dual effect results in two high tides occurring simultaneously: one on the side facing the Moon and the other on the opposite side. Between these high tides, low tides occur in areas where the water level is pulled away.
What Causes High and Low Tides?
High and low tides are caused by the gravitational interplay between the Earth, Moon, and Sun. While the Moon is the primary driver of tides, other factors such as the Earth's rotation, the Sun's gravitational pull, and the shape of the coastline also play significant roles.
Factors Influencing High and Low Tides
- Earth-Moon Distance: The closer the Moon is to the Earth, the stronger its gravitational pull, leading to higher high tides.
- Earth's Rotation: The Earth's rotation causes water to move, creating the cyclical pattern of high and low tides.
- Coastal Geography: The shape and depth of the coastline can amplify or diminish tidal effects.
The Role of the Moon in Lunar Tides
The Moon plays a pivotal role in the occurrence of lunar tides. Its gravitational pull directly influences the movement of water on Earth. Without the Moon, the tidal range would be significantly smaller, and the Earth's natural systems would be drastically altered.
How Does the Moon's Orbit Affect Tides?
The Moon's elliptical orbit around the Earth means that its distance from Earth varies. When the Moon is closest to Earth (perigee), its gravitational pull is stronger, resulting in higher high tides, known as perigean tides. Conversely, when the Moon is farthest from Earth (apogee), its gravitational influence is weaker, leading to lower high tides.
How Solar Tides Interact with Lunar Tides?
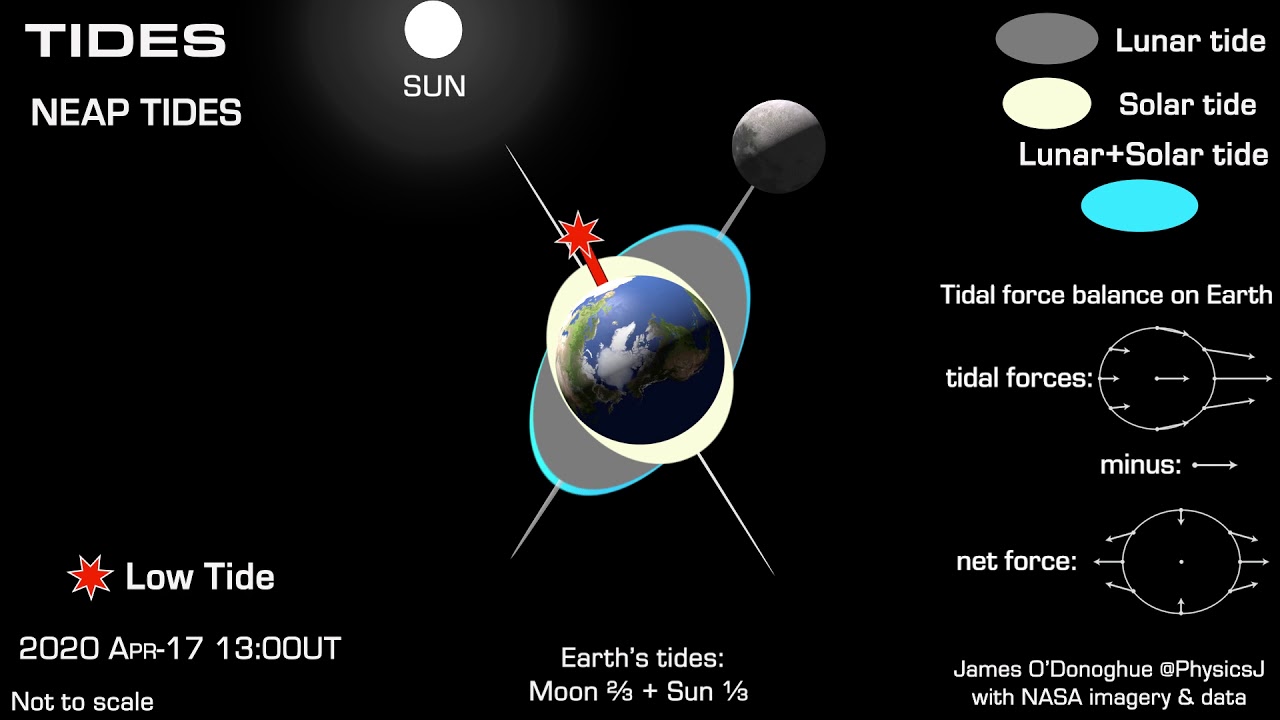
Solar tides, caused by the Sun's gravitational pull, interact with lunar tides in complex ways. When the Sun, Moon, and Earth align, their gravitational forces combine to create stronger tides. These are known as spring tides. Conversely, when the Sun and Moon are at right angles to each other, their gravitational forces partially cancel out, resulting in weaker neap tides.
The Interplay Between Solar and Lunar Forces
The interaction between solar and lunar tides highlights the dynamic nature of Earth's tidal system. This interplay not only affects the amplitude of tides but also their frequency and timing.
Spring and Neap Tides Explained
Spring and neap tides are two distinct types of tidal patterns that occur due to the alignment of the Earth, Moon, and Sun. Understanding these tides is crucial for predicting tidal behavior and its impact on coastal areas.
What Are Spring Tides?
Spring tides occur during the new moon and full moon phases when the Earth, Moon, and Sun are aligned. This alignment amplifies the gravitational forces, resulting in higher high tides and lower low tides.
What Are Neap Tides?
Neap tides, on the other hand, occur during the first and third quarter moon phases when the Earth, Moon, and Sun form a right angle. This alignment weakens the gravitational forces, leading to lower high tides and higher low tides.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are lunar tides? Lunar tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused primarily by the Moon's gravitational pull on Earth.
- How often do lunar tides occur? Most coastal areas experience two high tides and two low tides approximately every 24 hours and 50 minutes.
- What is the difference between spring and neap tides? Spring tides are stronger tides occurring during the new and full moon phases, while neap tides are weaker tides occurring during the first and third quarter moon phases.
- How do lunar tides affect marine life? Lunar tides influence marine life by affecting feeding, breeding, and migration patterns.
- Can lunar tides impact human activities? Yes, lunar tides can impact human activities such as fishing, shipping, and coastal development.
- Are lunar tides predictable? Yes, lunar tides are highly predictable due to their cyclical nature and the ability to calculate the positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun.
Conclusion
Lunar tides are a remarkable natural phenomenon that underscores the interconnectedness of Earth's systems and its celestial neighbors. From their influence on marine life and coastal ecosystems to their historical and cultural significance, lunar tides play a vital role in our understanding of the natural world. By studying and appreciating these rhythmic movements, we not only gain insights into the mechanics of our planet but also learn to live in harmony with its ever-changing environment.